Technical Material
UPS, inverter, rectifier, high-voltage power supply, etc.
Cautions for Use of a Cooling Fan in the Vicinity of a Power Switching Circuit
(prevention of electrolytic corrosion)
If a fan is installed near a large-power or high-voltage switching circuit, the heavy electromagnetic noise resulting from electromagnetic induction in such circuits or the influence of high-frequency noise imposed through the power line of the fan may induce current through the shaft bearing of the fan. Such current may damage the oil film on the bearing and even the friction surface of the bearing. This adverse effect is known as "electrolytic corrosion of the fan. "Electrolytic corrosion affects the smooth revolution of the fan and may reduce its service life. An audible symptom is unusual noise emitted from the fan. This adverse effect is often observed and may partly be explained by the practice of mounting high-density parts, which reduces the gap between the switching circuits and the fan and the use of higher switching frequencies apt to provoke induction. Data processing/communications devices that operate at low voltages are not liable to electrolytic corrosion since they generate less electromagnetic noise.
Fans without anti-corrosion features installed near components that generate electromagnetic noise, such as inverter controllers, are liable to experience electrolytic corrosion.
| No. | Use | Period until the occurrence of unusual noise |
| 1 | Switching power supply | 6 months to 2 years |
| 2 | UPS | 6 months to 2 years |
| 3 | General-purpose inverter | 1 to 1.5 years |
| 4 | Air cleaner | 2 to 3 months |
| 5 | Inverter for LCDs | 6 months |
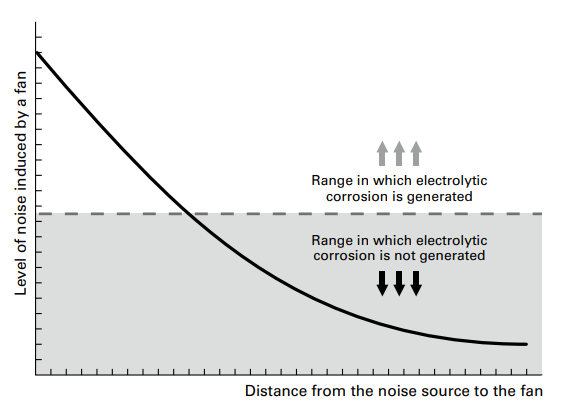
The curve shown in the graph below represents the relationship between the level of the electromagnetic noise induced by a fan and the distance from the fan to the noise source.
Occurrence of electrolytic corrosion Pattern 1
- 1. The fan gets charged with high-frequency electricity by high-frequency noise (electric field/magnetic field) generated in the switching circuit.
- 2. Because of high-frequency electricity charged in the fan, an electric current flows through the bearing of the fan.
- 3. The electric current breaks the oil membrane on the surface of the bearing and the bearing gets abraded (electrolytically corroded).
- 4. This symptom often occurs in equipment in which switching circuits are sped up and implemented in high density.
- 5. Countermeasure 1: To provide a shield plate(1) inside the fan (The plate should be such that does not interfere with airflow).
- 6. Countermeasure 2: To use a fan with ceramic bearings.
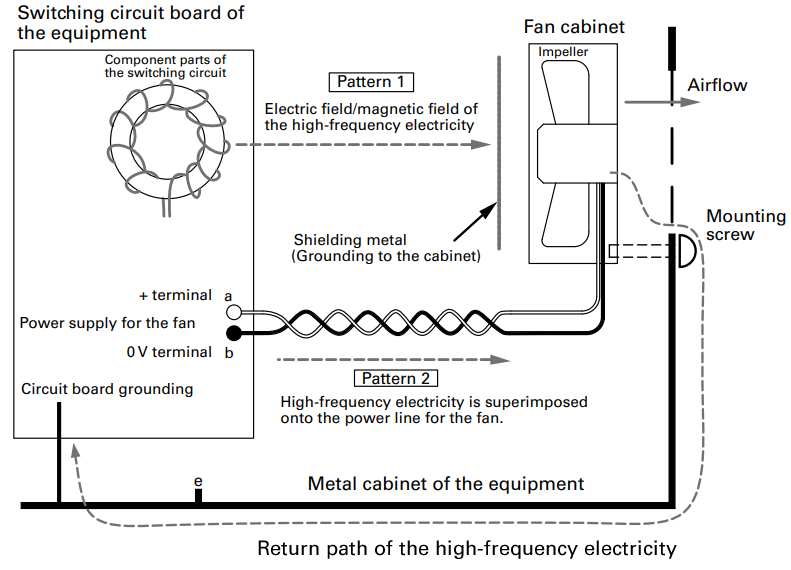
Occurrence of electrolytic corrosion Pattern 2
- 1. High-frequency electricity flows from the circuit board into the inside of the fan superimposed with the power line for the fan.
- 2. High-frequency electricity that has entered into the fan flows through the bearing.
- 3. Oil membrane on the surface of the bearing gets broken and the bearing gets abraded (electrolytically corroded).
- 4. Countermeasure 1: To remove high-frequency component between terminals "a" and "b", "a" and "e" and "b" and "e" of the power supply for the fan, or to insert a filter(2) into the power line for the fan.
- 5. Countermeasure 2: To use a fan with ceramic bearings
- 6. Cables should be twisted in order to decrease induction to the power line for the fan.
(1) Shielding metal plate
As an electromagnetic shield metal, "EMC Guard" is available from our company.
Certain shielding effect can be expected from mounting a general-purpose finger guard inside the fan. In each case, grounding to the cabinet is required.
(2) Filter
Insert a common mode filter when the high-frequency electricity is superimposed on both lines "a" and "b" in the same phase and, if not, insert a normal mode filter.
- Relocate fans far from all electromagnetic noise sources.
- Attach an EMC guard to ordinary fans. This should have an effect on electromagnetic noise due to radiation.
- As a power supply, the fan is wired from a circuit for which noise is not superimposed.
- Against heavy electromagnetic noise (electromagnetic induction) and conductive noise from the power supply line for a fan, we recommend the use of an "Electrolytic corrosion proof fan" with ceramic bearing.
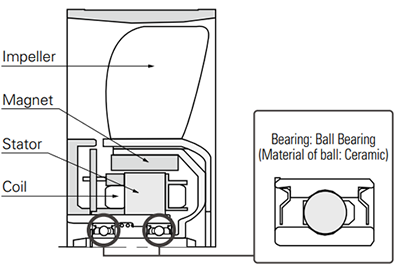
This cooling fan prevents electrolytic corrosion of bearings even under conditions where electromagnetic noise is generated. Electrolytic corrosion of ball bearings is prevented by using ceramic balls in ball bearings. The ceramic material is an insulating material.
Component diagram
Caution
Electrolytic Corrosion Proof Fan has been designed to prevent the electrolytic corrosion of ball bearings in the fan, but this does not guarantee that the fan will operate normally under conditions where there is strong electromagnetic noise.
Please be sure to fully evaluate the value of fan malfunction due to noise in advance.
Last updated: November 2025












